From a connected chain
Setting up Flows from Other Chains
Intento makes it easy to create flows—not just locally, but also from any chain connected via IBC. You can submit flows using:
- Intento Portal
- The IntentoJS front-end library
- The CLI
- Or directly from another chain using the ICS20 interchain token transfer standard.
Creating Flows with ICS20 Transfers
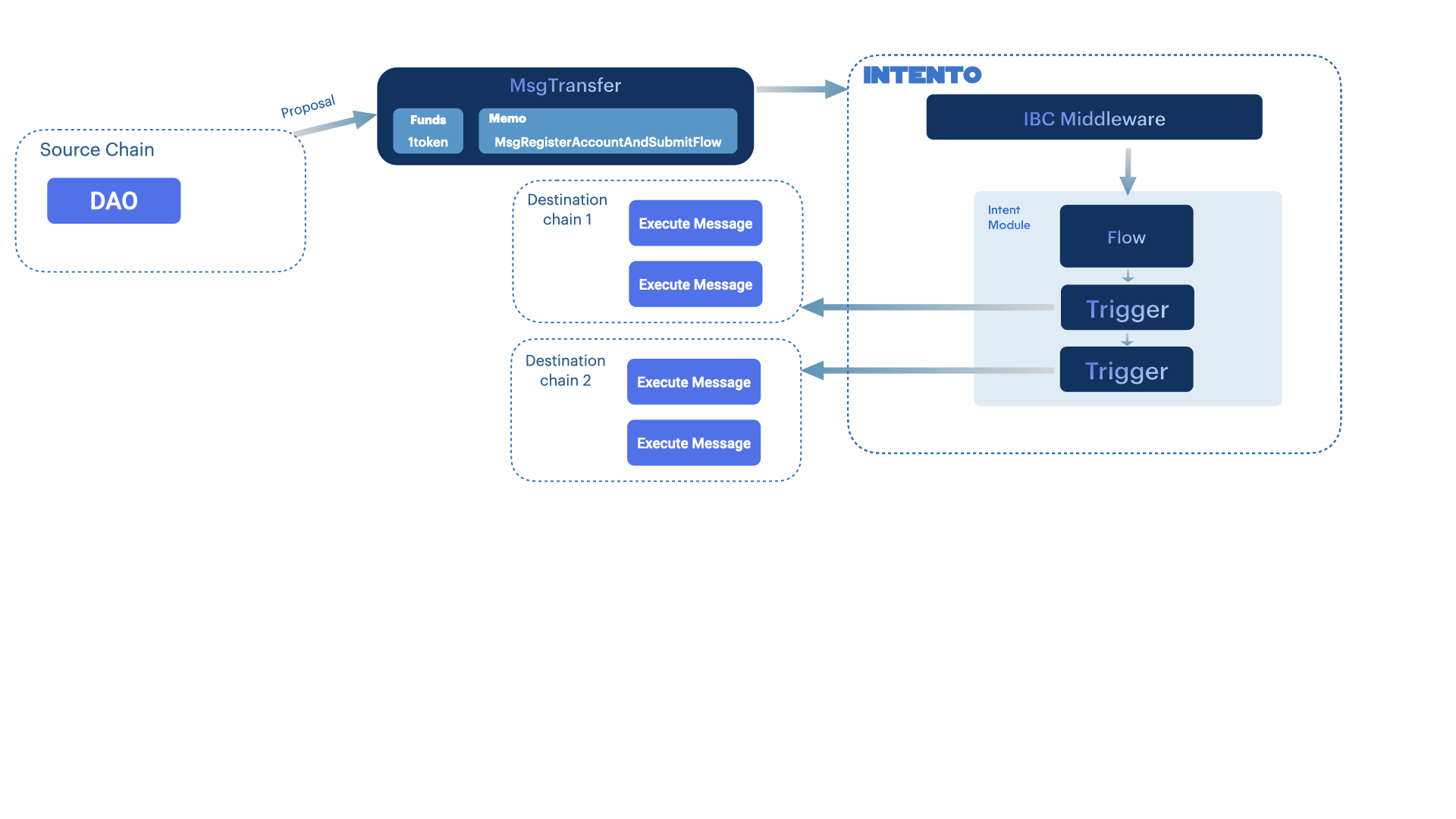
With Intento's custom IBC middleware, flows can be triggered by sending a regular ICS20 token transfer with a JSON memo. No new message types or protobuf encoding is required. This makes integration simple—even from a TypeScript frontend.
Instead of just transferring tokens, the ICS20 packet can include a flow definition in its memo field. Intento’s middleware will detect this and convert it into a MsgSubmitFlow or MsgRegisterAccountAndSubmitFlow.
This makes it possible to trigger complex intent-based actions—such as executing smart contracts, querying data (via ICQ), setting conditions, or running feedback loops—without ever leaving the originating chain.
A Note on Ownership and Security
One challenge is ownership. Normally, the ICS20 sender is considered the owner of the flow. But because IBC packets can be spoofed by malicious or misconfigured chains, trusting the sender blindly isn’t safe.
Intento solves this with a secure design:
- If the flow contains actions that execute on the same connection it came from, then the chain is treated as trusted, and the sender address is accepted as the owner.
- If not, a placeholder owner is created by hashing the sender and connection info, and the flow is still valid but restricted in terms of what it can control.
This ensures both trust and flexibility, without sacrificing user experience.
Why This Matters
This system unlocks powerful use cases across any chain connected to Intento:
- Automate token swaps, vesting, or payroll
- Call smart contracts cross-chain
- Perform ICQ and conditional flows
- Create advanced flows with feedback loops
- Delegate control to interchain accounts without needing governance votes for every step
Whether you're building wallets, automation tools, or interchain dApps—flows can now be triggered from anywhere, securely and easily.
ICS20 Standard
With Intento’s ICS20 middleware, you can submit flows directly from another chain by simply sending a token transfer with a memo field. The middleware interprets the memo and converts it into a MsgSubmitFlow.
ICS20 is an interchain standard for transferring fungible tokens via IBC. Using this standard, flows can be initiated just by including JSON-encoded flow metadata in the memo field of the ICS20 transfer message. This avoids the need for new message types or protobuf encoding – it's a fully compatible, low-friction integration.
Under the Hood
Example structure derived from an ICS20 memo:
msg := MsgSubmitFlow{
Owner: "into1-hash-of-channel-and-sender" OR packet.data.memo["flow"]["owner"],
Msgs: packet.data.memo["flow"]["msgs"],
FeeFunds: sdk.NewCoin{
Denom: ibc.ConvertSenderDenomToLocalDenom(packet.data.Denom),
Amount: packet.data.Amount,
},
// Additional metadata fields...
}
This enables secure, easy-to-integrate, and fully interchain-compatible flow orchestration – all while preserving a smooth developer experience.
ICS20 packet structure
So given the details above, we propogate the implied ICS20 packet data structure. ICS20 is JSON native, so we use JSON for the memo format.
{
//... other ibc fields that we don't care about
"data": {
"denom": "INTO denom on counterparty chain (e.g. ibc/abc...)",
"amount": "1000", //for execution fees
"sender": "...",
"receiver": "A INTO addr prefixed with into1",
"memo": {
"flow": {
"msgs": [
{
"@type": "/cosmos.somemodule.v1beta1.sometype"
//message values in JSON format
}
],
"duration": "111h",
"start_at": "11h",
"interval": "11h", //optional
"label": "my_label", //optional
"owner": "into1address", //owner can be specified for flows to the same IBC connection
"cid": "connection-0", //connection ID is optional, omit or leave blank in case local INTO message.
"cp_cid": "connection-0", //counterparty connection ID is optional and is only needed to register ICA.
"register_ica": "false", //optional, set to true to register interchain account
//////configuration,optional
"save_responses": "true", //save message responses of Cosmos SDK v0.46+ chain output, defaults to false
"update_disabled": "true", //optional, disables the owner's ability to update the config, defaults to false
"stop_on_success": "true", //optional, defaults to false
"stop_on_fail": "true" //optional, defaults to false
}
}
}
}
An ICS20 packet is formatted correctly for submitting an flow if the following all hold:
memois not blankmemois valid JSONmemohas at least one key,"flow"memo["flow"]["msgs"]is an array with valid JSON SDK message objects with a key "@type" and sdk message valuessender == memo["flow"]["owner"]. Optional, an owner can be specified for flows to the same IBC connection.memo["flow"]["cid"]is a valid connection ID on INTO -> Destination chain, omit it for local INTO execution of the message.memo["flow"]["register_ica"]can be added, and true to register an ICA.
Fees are paid with a newly generated flow fee account.
If an ICS20 packet does not contain a memo containing "flow", a regular MsgTransfer takes place. If an ICS20 packet is directed towards flow, and is formated incorrectly, then it returns an error. Here’s an improved version of the example with clearer language, structure, and formatting:
Example: DAO Integration
Overview
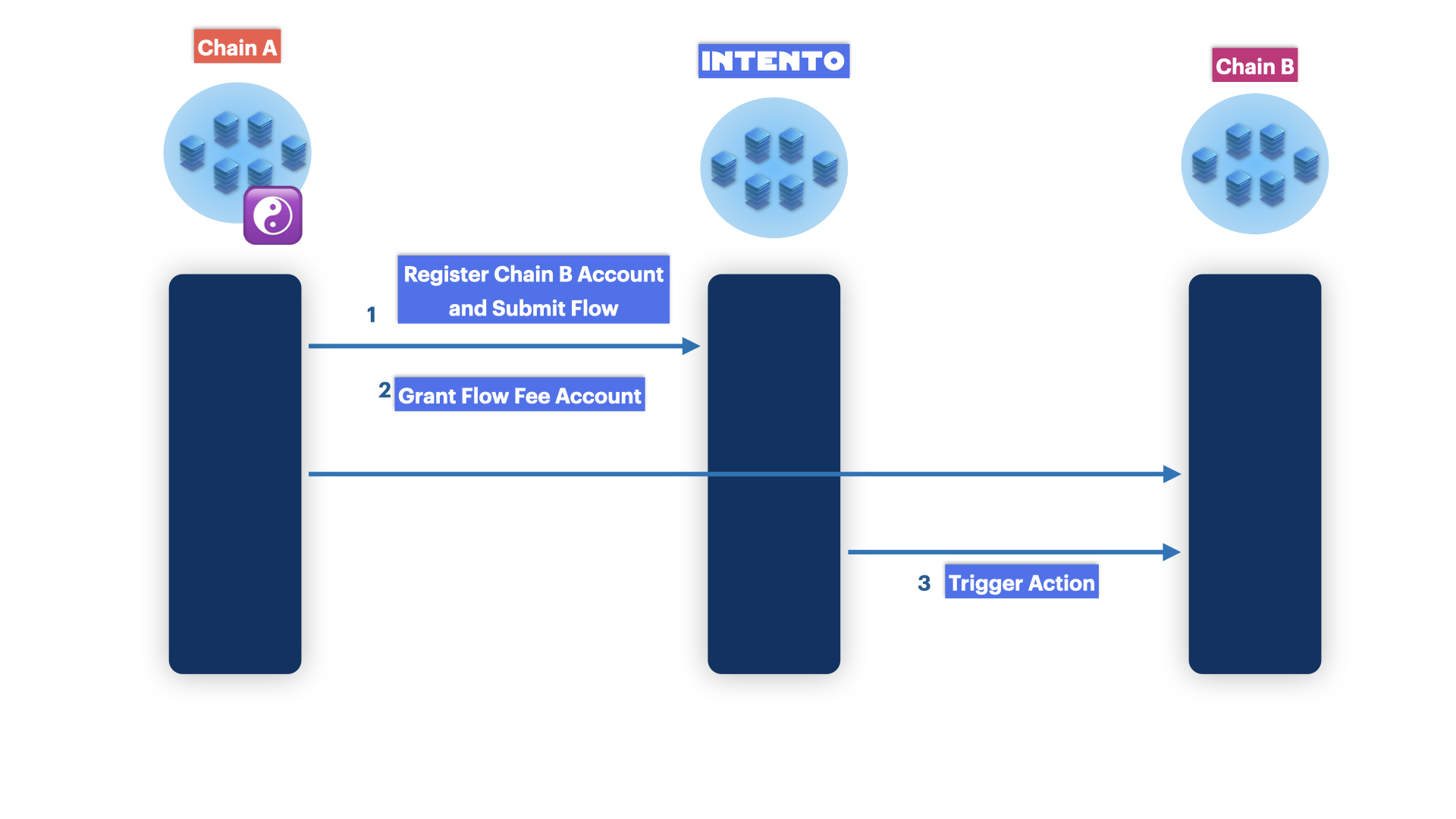
Using ICS20 to set up Intent-based flows is for users familiar with ICS20 transfers and Authz permissions. Our ICS20 middleware is designed to allow DAOs to submit flows, which can be done locally on Intento or on a destination chain. This can also be the source chain.
There are several caveats when setting up flows with ICS20. When automating on a destination chain for the first time, two messages are required to activate the flow. One flow sets up the flow and creates an Interchain Account on Intento, while the other sets permissions and sends funds to the Interchain Account on the destination chain.
In this example, we will demonstrate how a DAO can integrate with Intento by automating the payment process to a service provider.
Scenario: DAO Payment to Service Provider
The DAO wishes to pay Service Provider ABC monthly for their services in TOKEN1. The DAO holds TOKEN2 and NTRN.
Service Provider ABC invoice example
In this case, the DAO triggers a recurring swap of TOKEN2 for TOKEN1 on the decentralized exchange "DEX" and automatically sends the tokens to Service Provider ABC.
This setup is an ideal use case for Intento, as it involves asset movement between chains and accounts, while the DAO maintains control of the tokens. Since the flows are on-chain, the process is fully decentralized and does not require third-party trust.
The DAO can appoint an owner to manage the flow or use a placeholder account on Intento to remain in full control.
Proposal Details
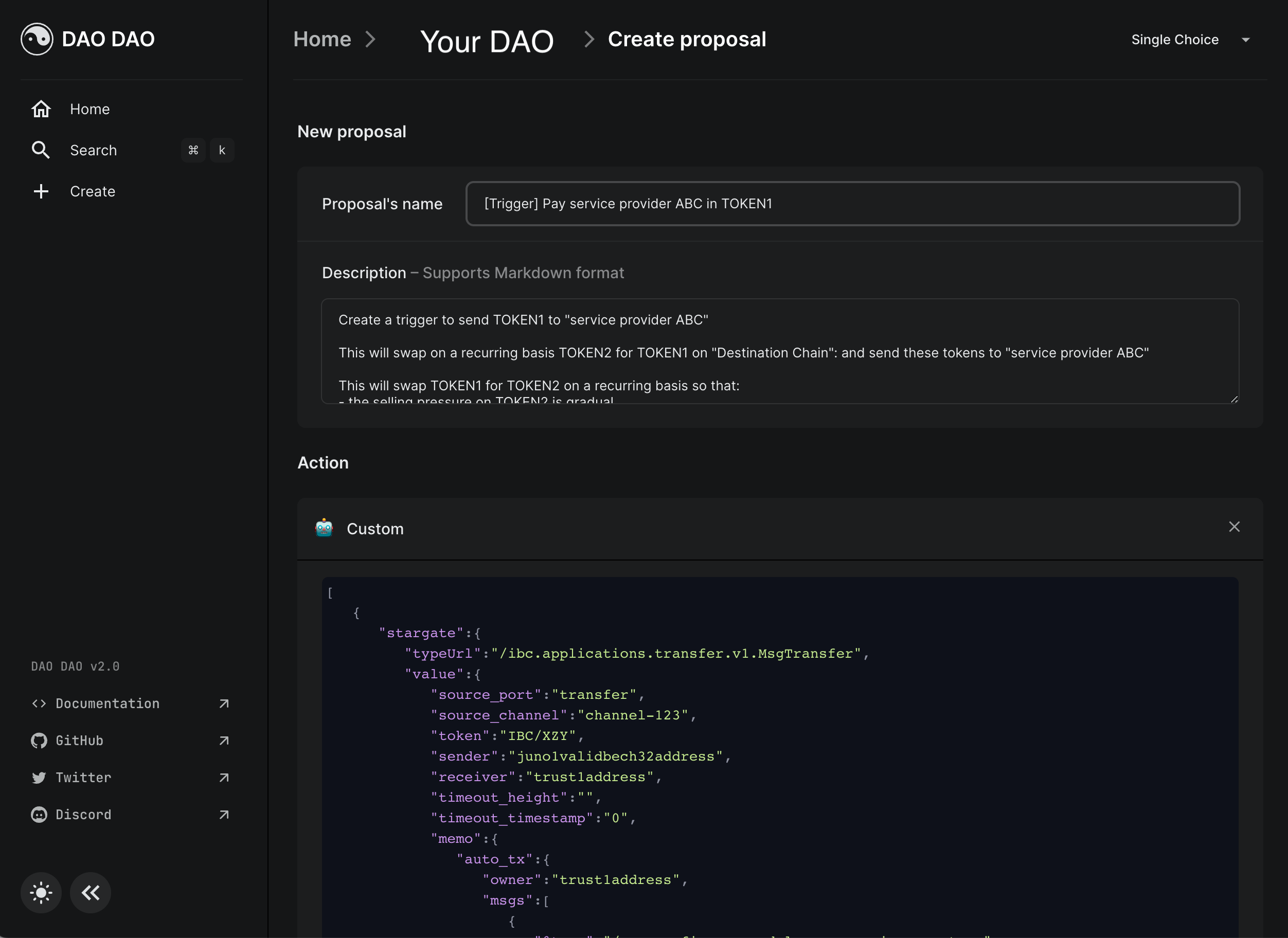
In this example, the DAO submits a proposal with the following name and description:
Proposal Name:
[Trigger] Pay Service Provider ABC in TOKEN1
Proposal Description:
Submit a flow to send TOKEN1 to "Service Provider ABC."
This flow will swap TOKEN2 for TOKEN1 on DEX "DEX" on the Destination Chain and automatically send these tokens to "Service Provider ABC." By performing this swap on a recurring basis, we achieve:
- Gradual selling pressure on TOKEN2
- Maintaining positive cash flow
This trigger on Intento automates asset workflows, ensuring liquidity and financial stability for the DAO.
Having sufficient liquidity ensures smooth operations and financial stability, allowing the DAO to meet its obligations and grow sustainably. Proper liquidity management helps to pay expenses, invest in growth, and strengthen the DAO's reputation in the market.
1. Submitting the Flow
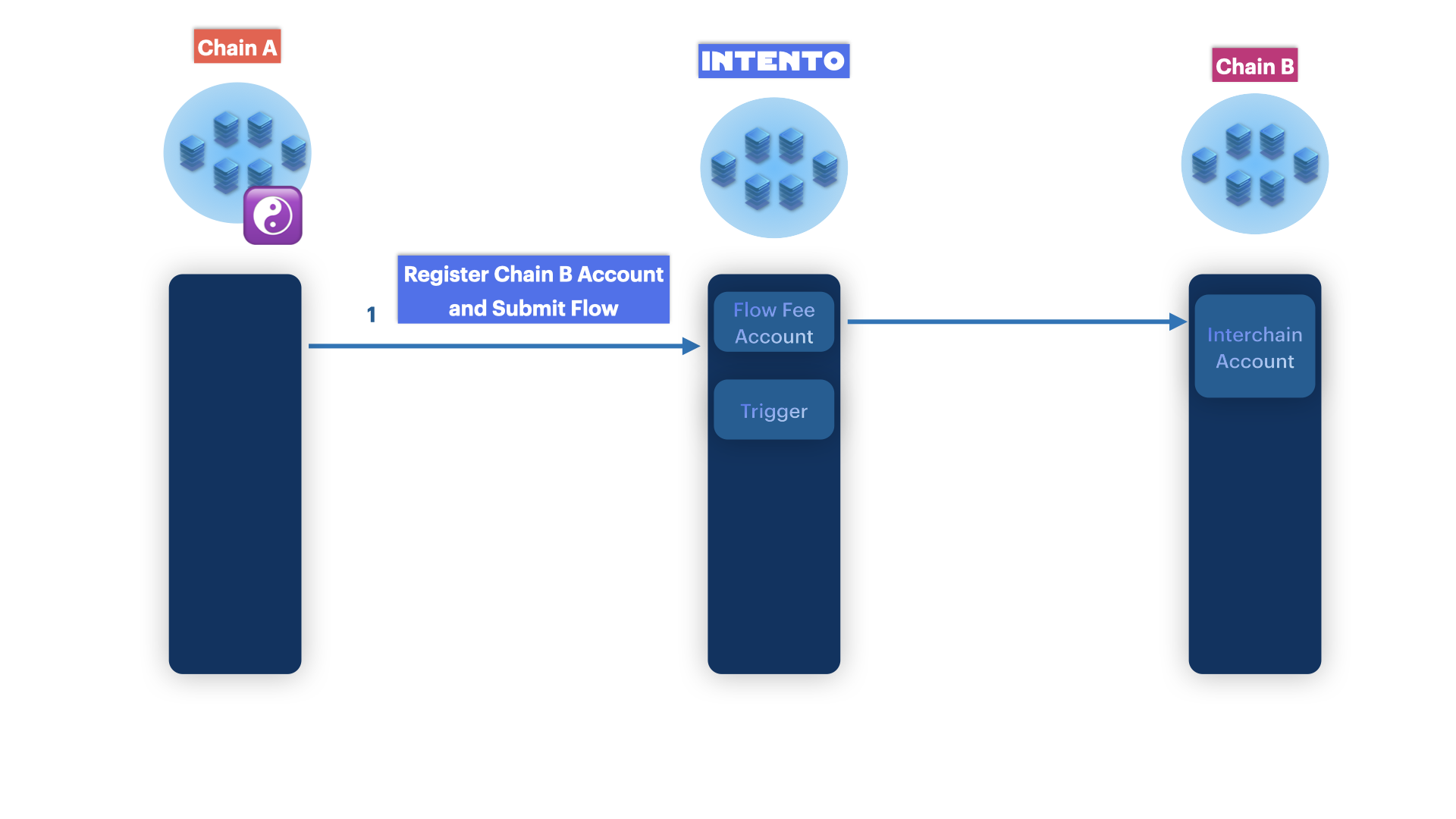
To submit the flow, the DAO creates a proposal with a custom message to execute. For a CosmWasm-based DAO like DAO DAO on Neutron, this message contains the ICS20 MsgTransfer. In the memo, the DAO provides flow details such as automated messages, time parameters, and a custom label.
Here’s an example of how the flow proposal message might look for a CosmWasm-based DAO:
[
{
"stargate": {
"typeUrl": "/ibc.applications.transfer.v1.MsgTransfer",
"value": {
"source_port": "transfer",
"source_channel": "channel-to-intento",
"token": { "denom": "ibc/....", "amount": "10" },
"sender": "neutron1validbech32address",
"receiver": "into1address",
"timeout_height": "0",
"timeout_timestamp": "0",
"memo": {
"flow": {
"owner": "into1address",
"msgs": [
{
"@type": "/someprefix.somemodule.someversion.sometype"
}
],
"duration": "111h",
"interval": "11h",
"start_at": "1677841601",
"label": "my_label",
"cid": "connection-0",
"register_ica": "true"
}
}
}
}
}
]
Important Notes:
- Ensure that
timeout_timestamportimeout_heightreflects the proposal's end time, or set both to0if no timeout is needed. - When creating the flow for the first time, make sure the
register_icafield is set to"true", which registers an Interchain Account on the destination chain.
A message within the flow["msgs"] array might look like this MsgSend:
{
"@type": "/cosmos.bank.v1beta1.MsgSend",
"amount": [
{
"amount": "70",
"denom": "stake"
}
],
"from_address": "ICA_ADDR",
"to_address": "some_destination_chain_address"
}
Alternatively, the DAO can use a custom smart contract message like SwapAndSendTo in a MsgExecuteContract message to swap TOKEN2 for TOKEN1.
{
"@type": "/cosmos.authz.v1beta1.MsgExec",
"msgs": [
{
"@type": "/cosmwasm.wasm.v1.MsgExecuteContract",
"msg": {
"swap_and_send_to": {
"input_token": "TOKEN2",
"min_token": "500",
"recipient": "neutron1_address"
}
},
"sender": "neutron1_address_dao",
"contract": "neutron1_address_swap_contract",
"funds": []
}
],
"grantee": "ICA_ADDR"
}
Write ICA_ADDR as a grantee or in other fields within the message, and Intento will parse the to-be-defined Interchain Account address.
You can also use MsgSwapExactAmountOut to swap tokens on decentralized exchanges like Osmosis or Dymension.
2. Setting Up Permissions and Funds
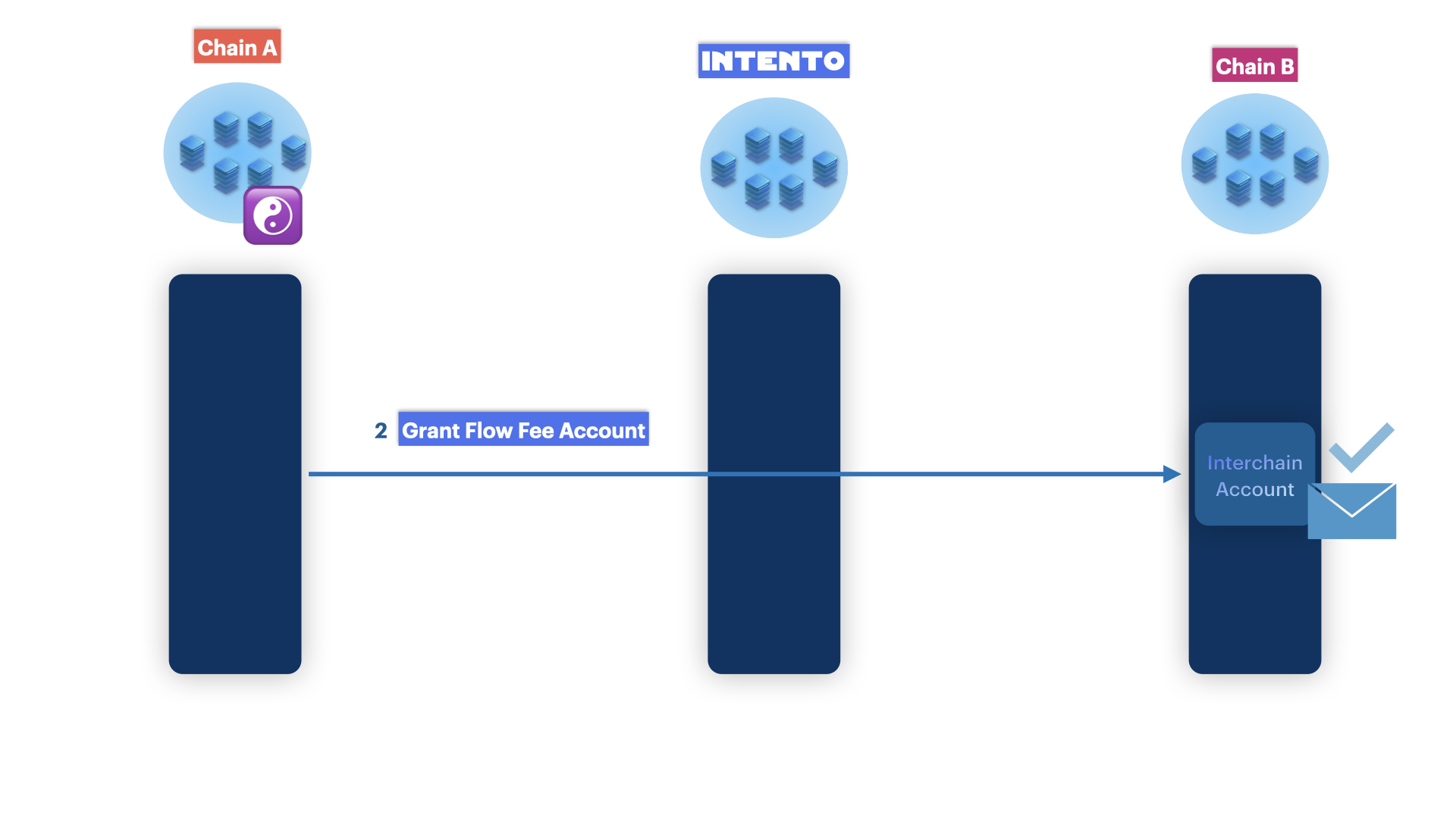
The Interchain Account (ICA) must be properly funded and authorized before it can execute the flow.
Paying for Fees
Flow fees on Intento are automatically paid from the funds sent via ICS20. For flows executed on the destination chain, the Flow Account on the destination chain should be funded with the destination chain's fee token.
If needed, a separate proposal can be submitted to send tokens (via MsgSend or MsgTransfer) to the destination chain's ICA address.
If the source and destination chains are the same, you can set up a FeeGrant for the ICA on the destination chain.
Setting Permissions
For flows on Cosmos chains, set up an AuthZ grant using MsgGrant. For EVM chains, you can give the flow account allowance for ERC20 tokens or approval for NFTs.
Once funds and permissions are set up, only one flow proposal is required to trigger the flow.
3. Managing Flows
You can manage your flows on Intento Portal, where you can create, view, update, and control your flows.